West Africa has been a vibrant hub of trade for centuries, connecting civilizations and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures. From the bustling markets of the ancient empires to the modern ports that dot its coastline, the region has played a pivotal role in shaping global commerce.
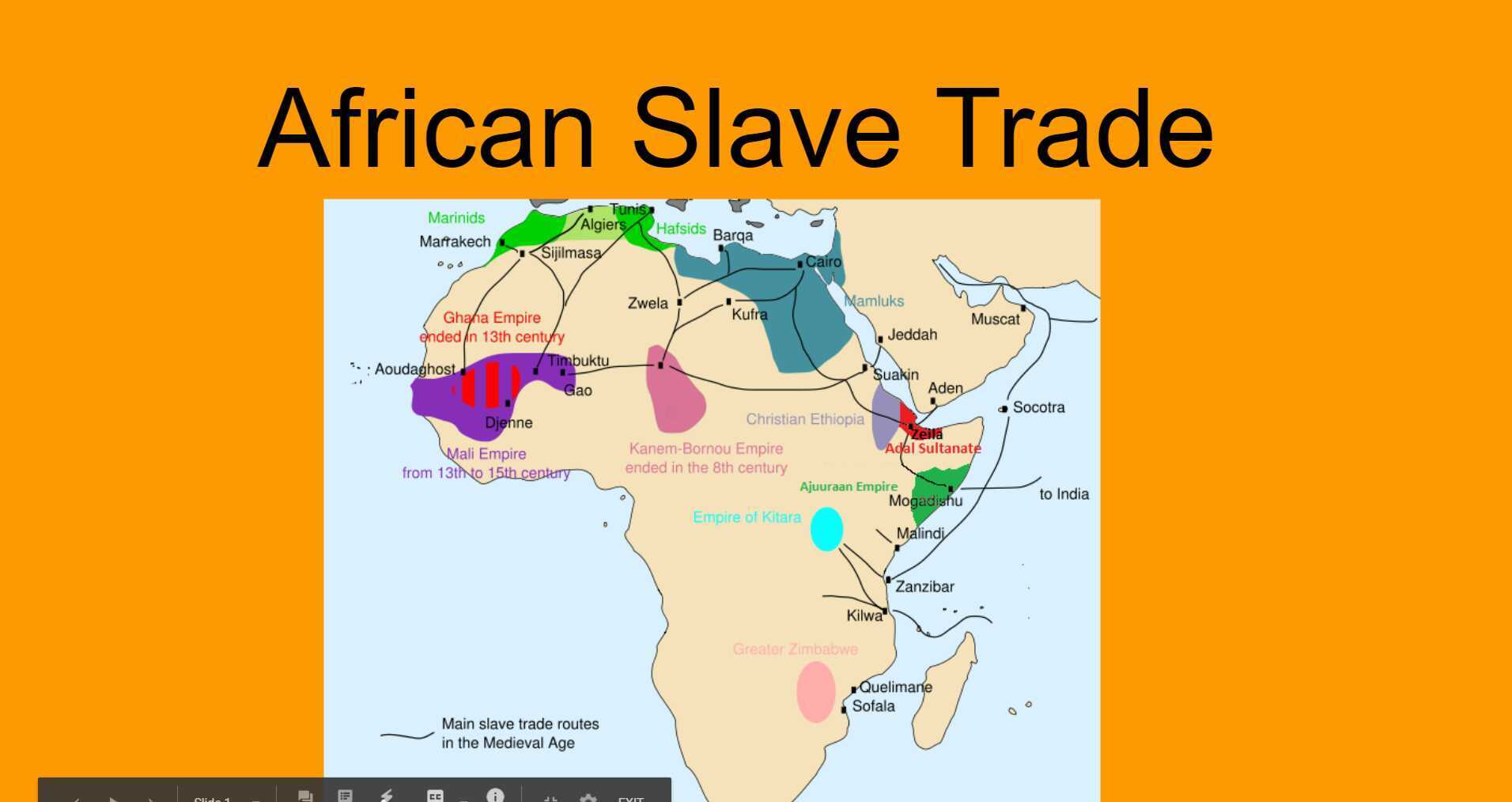
Image: screenpal.com
The trade routes that crisscrossed West Africa were the arteries of economic activity, transporting a vast array of products across vast distances. Gold, ivory, slaves, salt, and agricultural goods were among the most sought-after commodities, shaping the destiny of kingdoms and empires throughout the region.
The Golden Age of the Sahel Kingdoms
During the 8th century CE, the rise of the Sahel kingdoms ushered in a golden age of trans-Saharan trade. Ghana, Mali, and Songhai emerged as major trading centers, controlling the flow of gold, salt, and other goods between North Africa and West Africa. The prosperity of these empires fueled the development of sophisticated urban centers, cultural achievements, and political stability.
The Advent of the Atlantic Slave Trade
In the 15th century, the arrival of European traders had a profound impact on West Africa. The transatlantic slave trade became a major driver of commerce, with millions of people forcibly taken from their homes to be sold in the Americas. This tragic chapter in history had a devastating impact on West African societies, disrupting economies and leaving an enduring legacy of trauma.
Colonial Trade and the Scramble for Africa
The 19th century witnessed the colonization of West Africa by European powers. The colonial era brought new forms of trade, with European companies establishing plantations and exploiting natural resources. The scramble for Africa led to the demarcation of borders that often divided traditional trading networks and disrupted local economies.

Image: exhibitions.abdn.ac.uk
Independence and Economic Diversification
The post-independence era saw West African nations strive to diversify their economies and reduce dependence on the export of raw materials. Industrialization and the development of new industries became a priority, with varying degrees of success. Regional economic organizations were formed to promote cooperation and cross-border trade.
Contemporary Trade in West Africa
Today, West Africa is experiencing a resurgence of trade, driven by economic liberalization, improved transportation infrastructure, and the growth of regional markets. The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) has played a vital role in fostering regional integration and facilitating trade across borders.
The Future of Trade in West Africa
The future of trade in West Africa holds immense opportunities for growth and development. The region’s vast natural resources, young population, and strategic geographic location make it a prime destination for investment and trade. By leveraging technology, infrastructure, and sustainable practices, West Africa can harness the transformative power of trade to uplift its people and shape a prosperous future.
Trade In West Africa
Conclusion
The trade in West Africa has been a complex and multifaceted tapestry that has shaped the region’s history, economy, and culture. From the ancient empires of Ghana and Mali to the modern challenges of globalization, trade has been a driving force in transforming the lives of its people. As the region looks ahead, embracing the opportunities and overcoming the challenges of contemporary trade, it can unlock its boundless potential and secure a vibrant and equitable future for its citizens.






