Introduction: The Global Marketplace of Currencies
The foreign exchange (forex) market stands as the world’s largest and most liquid financial market, eclipsing even the stock and bond markets combined. With a daily trading volume exceeding $6.6 trillion, forex serves as a vibrant platform where currencies are exchanged, enabling international commerce and investments. Understanding the mechanisms and dynamics of forex trading is paramount for individuals seeking exposure to global financial markets.
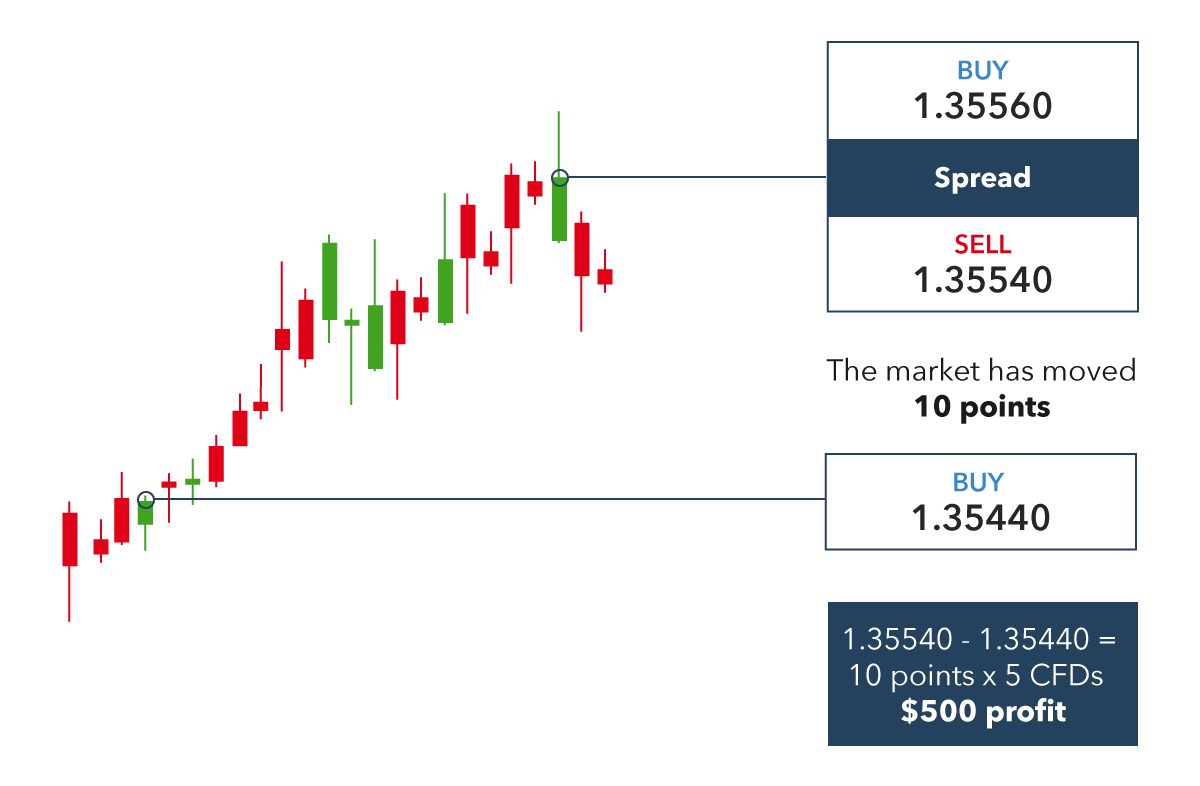
Image: cuartoymita.net
Main Body: Exploring the Mechanisms of Currency Exchange
Decentralized Trading: Unlike traditional stock exchanges, forex trading operates through a decentralized network of banks, brokers, and individual traders. It lacks a central location, ensuring round-the-clock accessibility.
Currency Pairs: Forex traders deal in currency pairs, representing the exchange rate between two different currencies. For example, the EUR/USD currency pair quantifies the amount of U.S. dollars (USD) needed to purchase one euro (EUR).
Leverage and Margin: Forex trading offers leverage, which allows traders to control positions larger than their account balance. However, leverage can amplify both profits and losses. Margin refers to the minimum capital required to hold a leveraged position.
Market Dynamics: Forex markets are primarily influenced by macroeconomic factors such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth. Political events, central bank announcements, and natural disasters can also impact currency values.
Retail and Institutional Trading: Forex trading attracts participants from both retail and institutional sectors. Retail traders typically trade smaller amounts, while institutional traders, including banks and hedge funds, execute high-volume deals.
Trading Strategies: Traders employ various strategies to capitalize on market dynamics. Technical analysis involves studying price charts to identify trends and patterns, while fundamental analysis focuses on economic data and news to predict currency movements.
Technological Advancements: The advent of electronic trading platforms has revolutionized forex trading. Automated systems, algorithms, and mobile apps have enhanced efficiency and accessibility.
Risks and Rewards: Like any investment, forex trading carries potential risks and rewards. Market volatility can lead to rapid price swings, posing the risk of losses. However, with proper risk management and discipline, traders can harness the market’s potential returns.

Image: forexrobotexpert.com
Forex Is Mostly Traded Via
Conclusion: Embracing the Global Currency Market
Forex trading provides a unique and exciting opportunity to participate in the global financial markets. Its decentralized structure, diverse currency pairs, and leverage options create a dynamic and challenging trading environment. Seasoned traders and novices alike should approach forex trading with a comprehensive understanding of its mechanisms, strategies, and risks. By embracing the complexities of the currency market, individuals can unlock the potential for financial success in this interconnected world.






