Introduction
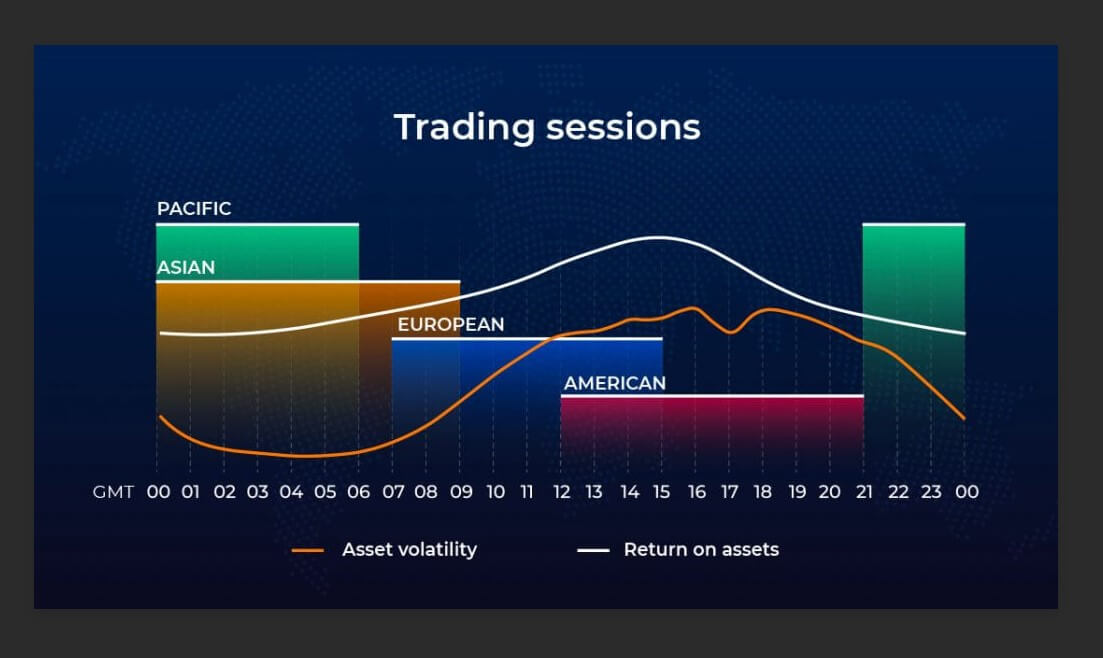
Image: www.forex.academy
The foreign exchange (forex) market is an ever-evolving financial arena where currencies are traded around the globe. The sheer volume of transactions and its impact on economies make forex a captivating field for investors, but navigating its complexities requires a keen understanding of risk management. This article delves into the fundamentals of forex markets and provides practical strategies to mitigate risk and maximize returns.
Navigating Forex Markets: A Global Arena for Exchange
The forex market is the world’s largest and most liquid financial market, estimated at over $6 trillion in daily trading volume. It operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, allowing for continuous currency transactions across different time zones. The major currencies traded in the forex market include the US dollar (USD), euro (EUR), Japanese yen (JPY), British pound (GBP), and Swiss franc (CHF). These currencies form various currency pairs, which are the foundation of foreign exchange trading.
Understanding Currency Pairs and Trading Basics
Currency pairs represent the value of one currency relative to another. For instance, the EUR/USD pair indicates how many US dollars it takes to buy one euro. Forex traders speculate on the price fluctuations of currency pairs, seeking to profit from changes in their exchange rates. Buying a currency pair anticipates its appreciation against the other currency, while selling a pair signifies the expectation of depreciation.
Strategies for Risk Management: Safeguarding Forex Investments
In the dynamic world of forex, risk management is paramount for preserving capital and achieving long-term profitability. Here are some essential strategies to mitigate risks:
-
Position Sizing: Calculate appropriate trade sizes based on your account balance and risk tolerance. Avoid risking more than a small percentage of your capital on any single trade.
-
Leverage Control: Leverage allows traders to increase their trading power by borrowing capital from a broker. While leverage can amplify profits, it also magnifies losses. Use leverage prudently and within your risk appetite.
-
Stop-Loss Orders: Set stop-loss orders to automatically close positions when the market moves against you. These orders limit potential losses by exiting trades at a predefined price level.
-
Hedging Positions: Offset potential losses by hedging your positions. This involves taking opposite trades in correlated currency pairs to reduce risk exposure.
-
Diversification: Spread your trades across different currency pairs and asset classes. Diversification reduces the impact of downturns in any particular market or currency.
-
Market Research and Analysis: Thoroughly analyze market trends, news, and economic data before making trading decisions. Keep abreast of global events that may impact currency valuations.
-
Risk Management Tools: Utilize risk management tools such as technical analysis and volatility indicators to identify potential trading opportunities and assess market risk.
Conclusion: The Path to Forex Mastery
Managing risk in forex markets is crucial for long-term success. By understanding the mechanics of currency trading and implementing effective risk management strategies, traders can navigate the complexities of global markets with confidence. Remember, forex mastery requires patience, discipline, and a commitment to continuous learning. Embrace risk management as an integral part of your trading journey, and you’ll be well-equipped to unlock the potential of forex markets while safeguarding your financial well-being.
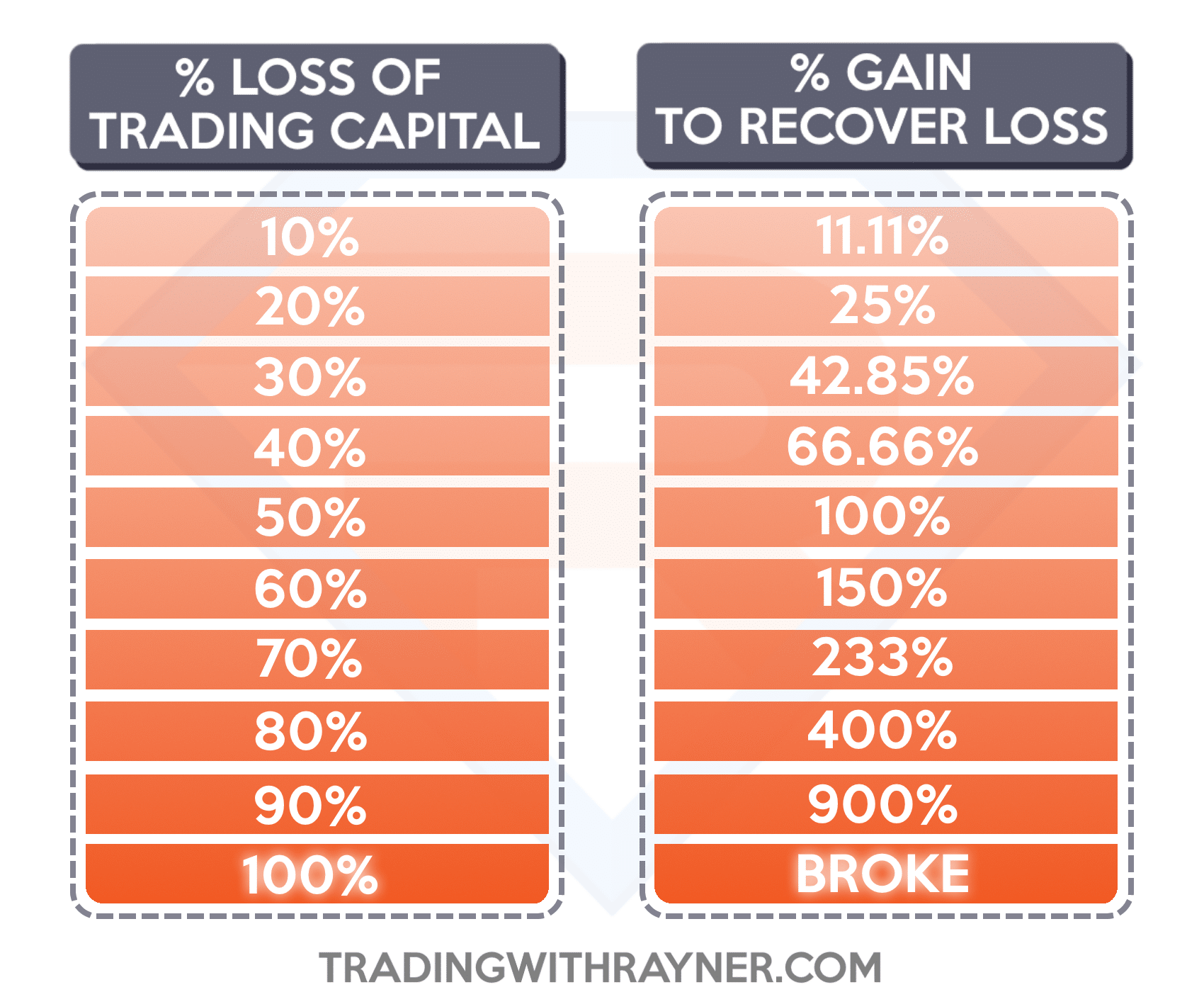
Image: www.tradingwithrayner.com
Forex Markets And Risk Management In Global Markets






