A Strategic Reserve for India
India’s foreign exchange reserves reached a historic milestone, crossing the $400 billion mark in December 2022. This significant achievement underscores the strength and resilience of the Indian economy and its preparedness to withstand global economic headwinds.
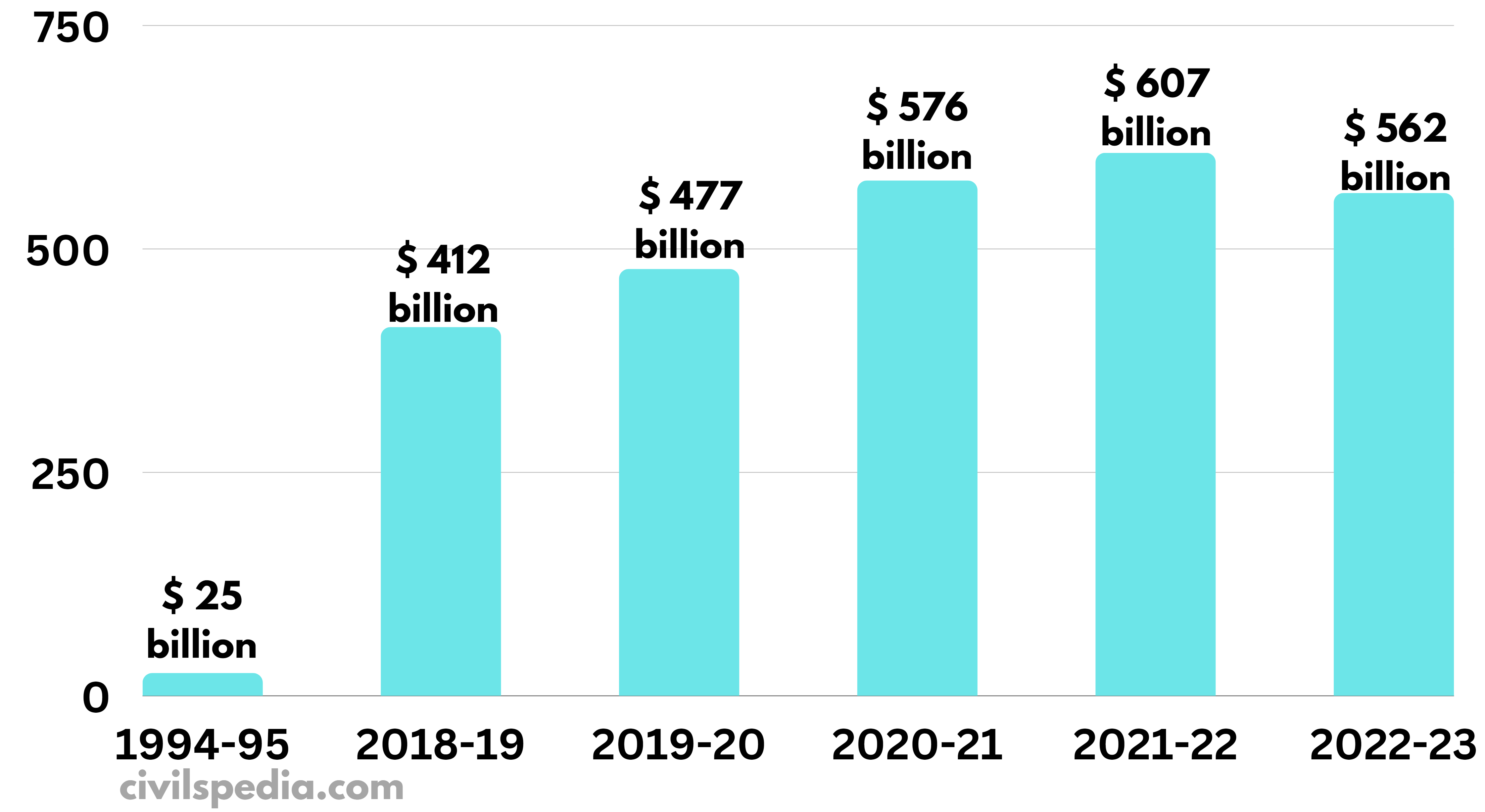
Image: civilspedia.com
Foreign exchange reserves, often referred to as forex reserves, represent the value of foreign currency assets held by India’s central bank, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). These assets include gold, Special Drawing Rights (SDRs), and foreign currency deposits held at other central banks.
Components of India’s Forex Reserves
Forex reserves play a crucial role in stabilizing India’s economy and providing a buffer against external shocks. The components of India’s forex reserves include:
- Gold: Gold constitutes a significant portion of India’s forex reserves, held in the form of gold bars and coins.
- SDRs: Special Drawing Rights are an international reserve asset of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and are included in India’s forex reserves.
- Foreign Currency Deposits: India holds a substantial amount of foreign currency deposits in various currencies, such as US dollars, euros, and Japanese yen, with central banks and other financial institutions abroad.
Advantages of Ample Forex Reserves
Maintaining a robust level of forex reserves offers several advantages for India:
- Stabilizing the Currency: Adequate forex reserves help stabilize the value of the Indian rupee by providing enough resources to intervene in the foreign exchange market if needed.
- Insulating the Economy from External Shocks: High forex reserves act as a safety net during economic downturns, enabling India to meet its external obligations and import essential goods.
- Promoting Trade and Investment: Ample forex reserves boost India’s credibility among international investors and lenders, encouraging foreign trade and investment.
Implications of High Forex Reserves
India’s record-high forex reserves have far-reaching implications:
- Economic Strength: High forex reserves are a testament to India’s economic strength and its ability to withstand global economic uncertainties.
- Reduced Risk and Enhanced Confidence: Ample forex reserves mitigate risks associated with India’s external debt and currency fluctuations, enhancing investor confidence.
- Monetary Policy Flexibility: The RBI gains increased flexibility in monetary policy decisions with robust forex reserves, allowing for proactive measures to manage inflation and economic growth.

Image: www.timesnownews.com
FAQs on Forex Reserves
Q: What factors contribute to increasing forex reserves?
A: Foreign investment, export earnings, and remittances from non-resident Indians are the primary factors that contribute to a rise in forex reserves.
Q: What are the implications of declining forex reserves?
A: Declining forex reserves can lead to currency depreciation, reduced import capacity, and macroeconomic instability.
Q: How are forex reserves used?
A: Forex reserves are primarily used to stabilize the currency, meet external obligations, and supplement foreign exchange holdings.
Forex Reserves May Hit 400 Indian Express
Conclusion
India’s foreign exchange reserves reaching $400 billion is a significant milestone that reflects the country’s economic resilience. Ample forex reserves provide stability to the Indian economy, buffer external shocks, and promote trade and investment. As India continues to navigate global economic challenges, maintaining robust forex reserves remains an important aspect of its financial strategy.
Are you interested in learning more about India’s forex reserves management and its impact on the economy? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below.






