India’s foreign exchange reserves have emerged as a crucial lifeline for the country’s economic health, serving as a buffer against global economic fluctuations and providing the foundation for borrowing. Understanding the relationship between forex reserves and India’s borrowing capacity is essential for policymakers and investors alike.

Image: www.dailypioneer.com
The Role of Forex Reserves in Borrowing
India’s forex reserves, held by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), consist of various foreign currencies, gold, and other assets. These reserves play a pivotal role in determining the country’s ability to borrow from international markets. The percentage of forex reserves on which India can borrow is usually determined by the perceived creditworthiness of the country, as well as the prevailing market conditions.
Typically, India can borrow up to a certain percentage of its total forex reserves. The Reserve Bank of India sets this limit to manage the country’s external debt and maintain currency stability. By establishing a conservative limit, India ensures that it does not become overly reliant on foreign borrowings and minimizes the risks associated with currency fluctuations.
Benefits of Forex Reserves
Maintaining adequate forex reserves offers several key benefits for India:
- Economic Stability: Forex reserves act as a shock absorber against external economic shocks. In Zeiten of global financial turmoil or a sudden outflow of foreign capital, forex reserves can be used to intervene in the foreign exchange market and maintain the stability of the rupee.
- International Creditworthiness: High forex reserves signal India’s financial strength and credibility to international investors. This can lower the cost of borrowing for Indian companies and the government, as investors perceive a reduced risk of default.
- Import Capacity: Forex reserves are essential for financing India’s imports, particularly essential commodities such as oil and gas. By maintaining adequate reserves, India can ensure its import needs are met without putting undue pressure on the currency.
Factors Influencing Borrowing Limit
The percentage of forex reserves on which India can borrow is influenced by various factors, including:
- Export Earnings: India’s ability to generate foreign exchange through exports strengthens its borrowing capacity. A sustained increase in export earnings can lead to higher forex reserves and a higher borrowing limit.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): FDI inflows also contribute to forex reserves and enhance India’s creditworthiness. A steady flow of FDI can boost India’s borrowing limit and reduce the need for external borrowings.
- Global Economic Conditions: Global economic conditions can impact India’s access to international borrowings. During periods of financial stress or rising interest rates, India’s borrowing limit may be reduced as investors become more risk-averse.
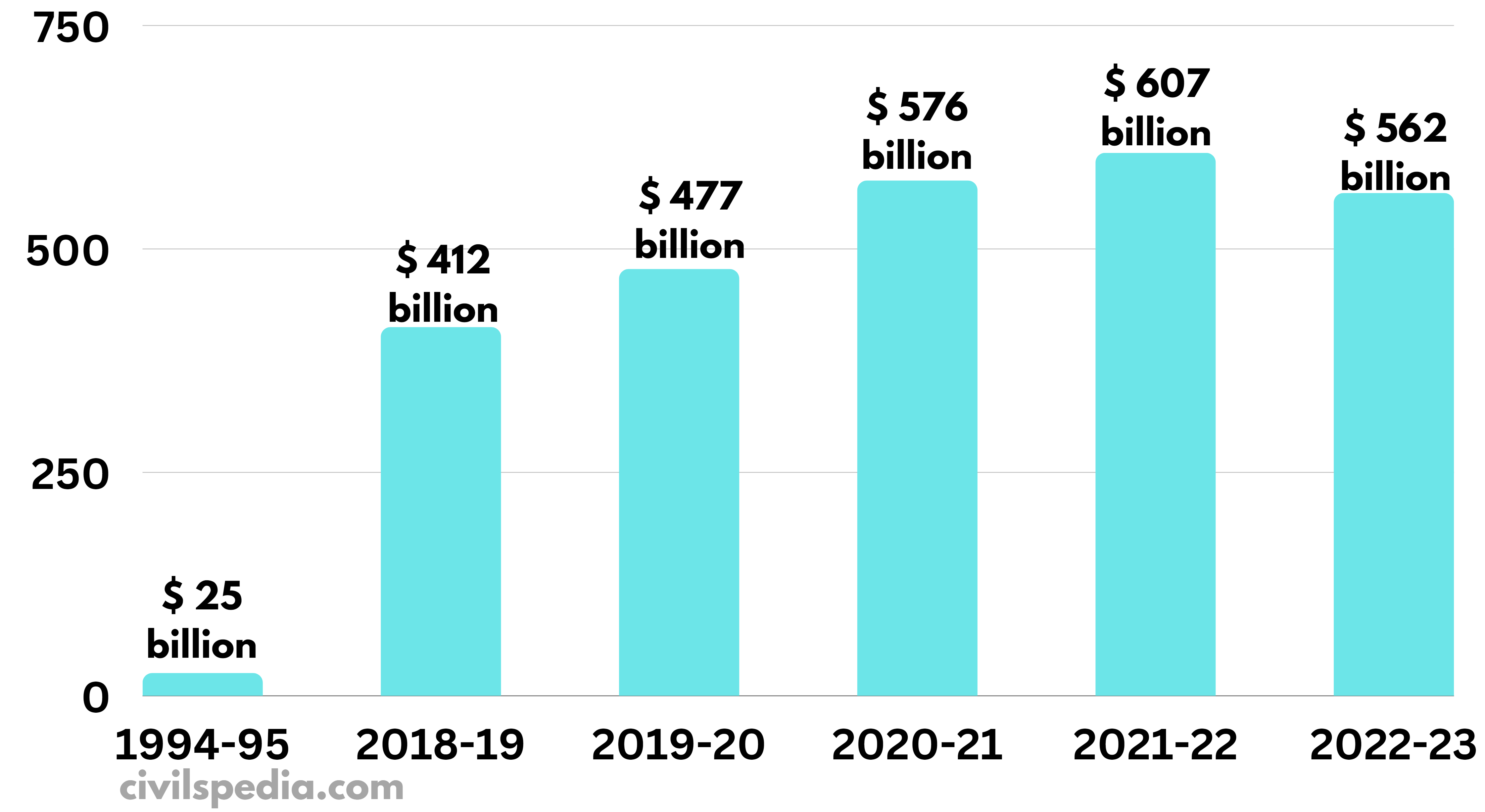
Image: civilspedia.com
Percentage Of Forex Reserve On Basis Which India Borrow
Conclusion
India’s forex reserves play a crucial role in shaping the country’s borrowing capacity and ensuring economic stability. By maintaining adequate forex reserves, India can mitigate external financial shocks, boost its creditworthiness, and meet its import needs. Understanding the relationship between forex reserves and borrowing is essential for policymakers to manage India’s external finances effectively and for investors to make informed decisions in the international financial markets.






