Across the vast expanse of the African continent, a mosaic of trading blocs has emerged as a testament to the spirit of cooperation and shared economic prosperity. These blocs, each with its unique mandate and membership, serve as vital platforms for fostering regional integration, boosting trade, and accelerating economic development.
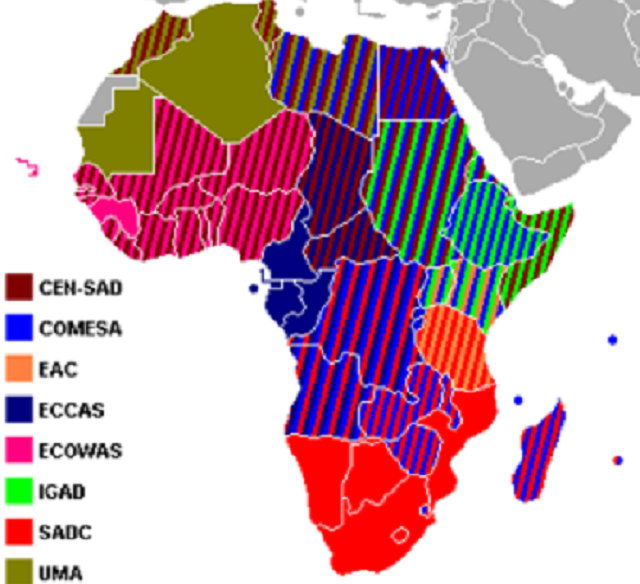
Image: www.chronicle.co.zw
Their formation reflects the shared recognition that economic fragmentation hinders Africa’s progress. By collaborating and leveraging their collective strengths, these trading blocs aim to create a more conducive environment for businesses to thrive, consumers to benefit from increased choice and affordability, and governments to reap the fruits of enhanced economic activity.
A Tapestry of Regional Cooperation
The African continent is home to several prominent trading blocs, each serving specific geographic and economic needs. Among the most notable are:
Southern African Development Community (SADC)
Established in 1994, SADC is the most populous trading bloc in Africa, encompassing 16 member states in Southern Africa. Its mission is to promote economic integration, peace, and security within the region.
Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
COMESA, established in 1994, comprises 19 member states in Eastern and Southern Africa. Its focus lies in developing a common market for the region, boosting trade, and harmonizing economic policies.
Image: www.gpb.org
East African Community (EAC)
The EAC, established in 1967, brings together six member states in East Africa. Its mandate includes fostering regional cooperation, economic integration, and political stability.
Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
ECOWAS, established in 1975, is the largest trading bloc in West Africa, comprising 15 member states. Its aim is to promote economic cooperation, regional integration, and monetary harmony.
Benefits of Regional Integration
The formation of trading blocs in Africa offers a multitude of benefits, including:
Increased Trade and Economic Growth
Trading blocs eliminate barriers to trade within their regions, facilitating smoother flow of goods and services. This increased trade leads to economic growth and job creation.
Enhanced Investment and Development
Trading blocs provide a more stable and predictable investment environment, attracting foreign and domestic capital. This investment supports infrastructure development, innovation, and economic diversification.
Political Stability and Economic Security
Economic cooperation and integration foster political stability and create a sense of common interest among member states. This reduces the risk of conflicts and enhances regional security.
Challenges and the Future
Despite their advantages, trading blocs in Africa also face challenges:
Internal Disputes and Conflicts
Internal disputes and conflicts can hinder regional cooperation and economic integration.
Inadequate Infrastructure
Insufficient infrastructure, such as transportation, communication, and energy, can hamper trade and limit the bloc’s effectiveness.
External Competition
Trading blocs in Africa face competition from global markets and other economic blocs. Navigating these external challenges is crucial for their sustained success.
Examples Of Trading Blocs In Africa
Conclusion
Trading blocs in Africa are indispensable to the continent’s economic growth and development. Through cooperation, shared vision, and the removal of barriers, these blocs have laid the foundation for a more cohesive and prosperous Africa. While challenges remain, the benefits of regional integration are undeniable. By addressing these challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities, Africa’s trading blocs have the potential to transform the continent into an economic powerhouse.






