Introduction
In today’s multifaceted financial landscape, exchange-traded funds (ETFs) have emerged as indispensable investment vehicles for both seasoned investors and investing enthusiasts. These versatile entities offer a convenient and often cost-effective way to tap into the full spectrum of asset classes and investment strategies. Whether you seek growth potential, income generation, or diversification, ETFs provide a tailored solution to suit your unique investment aspirations.
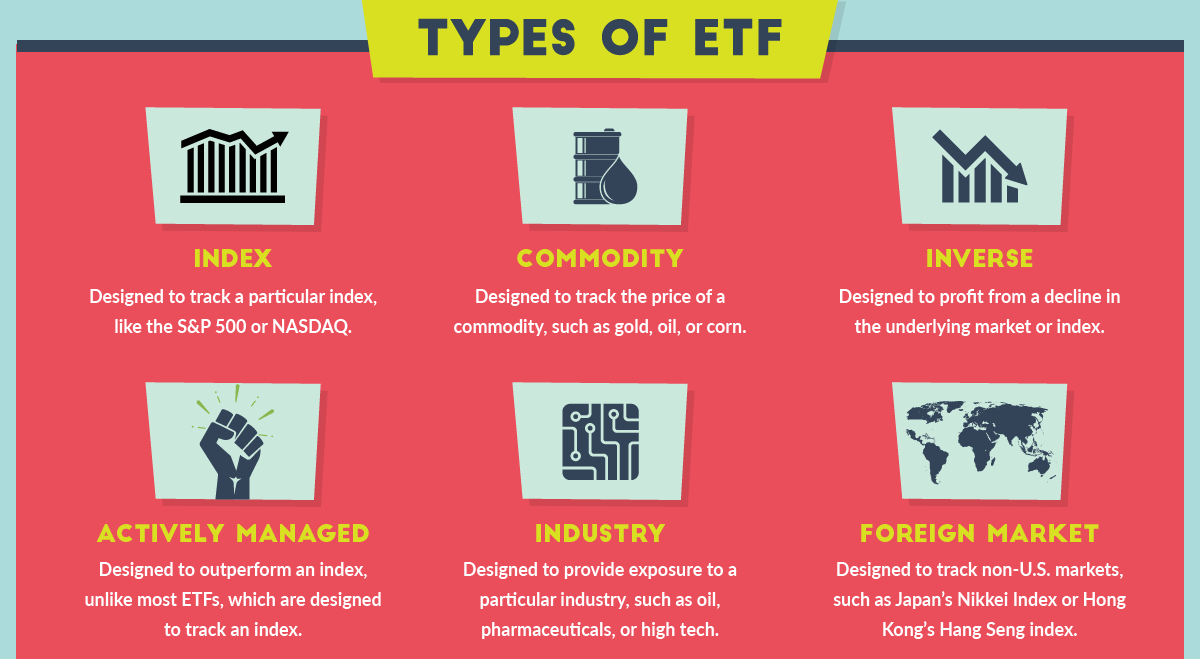
Image: www.visualcapitalist.com
This comprehensive guide will illuminate the labyrinthine realm of ETFs, navigating you through the intricate intricacies of their structure, types, and characteristics. By delving into their unique attributes, you’ll be equipped to make informed investment decisions that empower your financial journey.
Understanding the Anatomy of ETFs
Building Blocks of ETFs
Categories and Subcategories of ETFs: A Comprehensive Overview
Equity ETFs:
- Tracking a specific equity index (e.g., S&P 500)
- Sector-focused (e.g., technology, healthcare)
- Leveraged or inverse (designed for sophisticated investors)
- Diversified (providing broad exposure to multiple sectors)
Fixed Income ETFs:
- Invested in bonds of various maturities and credit ratings
- Income-oriented with regular interest payments
- Tax-efficient options available (e.g., municipal bond ETFs)
Commodity ETFs:
- Tracking a specific commodity (e.g., gold, oil)
- Provide exposure to physical commodities or futures contracts
- Used for hedging or speculative investments
International ETFs:
- Investing in stocks or bonds of companies outside the U.S.
- Exposure to foreign markets and currencies
- Opportunities for international diversification
Real Estate ETFs:
- Investing in real estate investment trusts (REITs)
- Rental income-generating assets
- Diversification from traditional equity investments
Currency ETFs:
- Tracking a specific currency (e.g., Euro, Japanese Yen)
- Used for currency trading or hedging

Image: medium.com
Emerging Trends and Frontiers in the ETF Market:
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) ETFs:
- Investing in companies with strong ESG practices
- Alignment with ethical and sustainability goals
Cryptocurrency ETFs:
- Tracking the price of cryptocurrencies (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum)
- Offering exposure to a new asset class
Active vs. Passive ETFs:
- Actively managed ETFs: Employ a team of portfolio managers making investment decisions
- Passively managed ETFs: Track a specific benchmark or index
Expert Insights and Investment Strategies:
Diversify Your Portfolio: ETFs provide instant diversification, reducing the risk associated with investing in individual stocks or bonds.
Lower Costs: ETFs often have lower expense ratios than traditional mutual funds, making them more cost-effective investment options.
Tax Efficiency: Certain ETFs, such as municipal bond ETFs, can offer tax advantages.
Flexibility and Liquidity: ETFs are traded on stock exchanges, providing investors with real-time pricing and the ability to buy or sell shares throughout the trading day.
Different Types Of Etfs
Conclusion:
ETFs have revolutionized the investment landscape, offering a highly diversified and flexible approach to meeting financial goals. This comprehensive guide empowers you to navigate the diverse range of ETFs and make informed investment decisions. By tapping into the expertise and strategies outlined in this article, you can unlock the full potential of ETFs and embark on a transformative investment journey.






