Introduction
The trans-Atlantic slave trade, a dark chapter in human history, cast a long shadow on Africa. Millions of innocent Africans were forcibly removed from their homes and sold into chattel slavery in the Americas, leaving an indelible mark on both continents.

Image: www.statista.com
Through the relentless efforts of enslaved Africans and the abolitionist movement, slavery was finally abolished. However, the scars of this abhorrent system run deep, continuing to shape the lives of people of African descent in the present day.
The Beginning of the Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade
The trans-Atlantic slave trade officially began in the 16th century when European traders established outposts along the coast of West Africa to acquire enslaved people. However, the slave trade had existed on the African continent for centuries before this, with Arab traders operating in East Africa.
The demand for enslaved laborers to work on plantations in the Americas, particularly in the Caribbean and South America, fueled the rapid expansion of the trans-Atlantic slave trade. Enslaved Africans were forced to endure unimaginable hardships during the perilous middle passage, the brutal journey across the Atlantic Ocean.
The Impact on Africa
Demographic and Economic: The loss of millions of young and able-bodied Africans left a profound demographic impact on their communities. Villages and societies were torn apart, and economic systems were disrupted. The slave trade also depleted the continent’s skilled workforce, hindering its development.
Social and Cultural: The slave trade profoundly impacted African societies and cultures. Families were separated, and traditional customs and values were undermined. Additionally, the slave trade fostered a stigma of inferiority among Africans, which had long-lasting effects.
Resistance and Abolition
Despite the horrors of enslavement, Africans never gave up their fight for freedom. From the slave revolts on ships to the establishment of maroon communities in the Americas, enslaved Africans exhibited extraordinary resilience and determination.
In Europe and North America, the abolitionist movement gained momentum in the 18th and 19th centuries, fueled by the Enlightenment and the growing recognition of human rights. Eventually, slavery was abolished in the British Empire in 1833 and the United States in 1865. However, the legacy of slavery continued to reverberate in both continents.
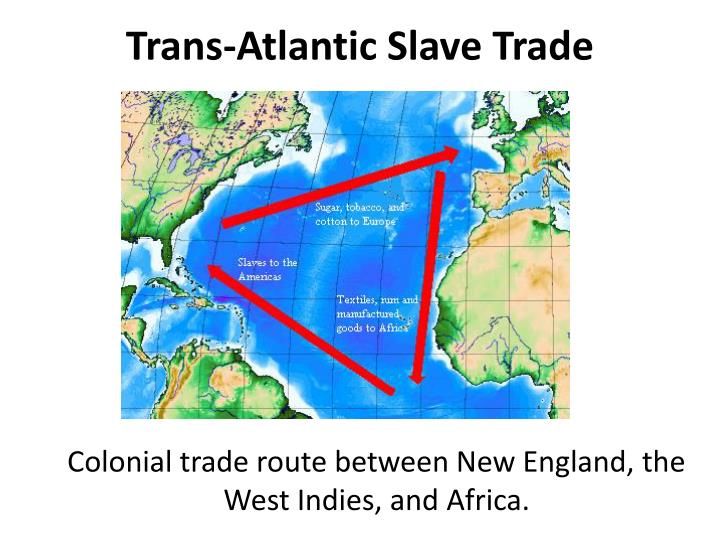
Image: www.slideserve.com
Latest Trends and Developments
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of interest in the trans-Atlantic slave trade. Scholars, historians, and activists have made significant contributions to our understanding of this complex and painful period in history.
Through research, documentaries, and museum exhibitions, the experiences of enslaved Africans are being brought to light. This increased awareness has led to efforts for reparations, reconciliation, and the preservation of slave trade-related sites.
Tips and Expert Advice
Educate Yourself and Others: Learn about the trans-Atlantic slave trade and its lasting impact. Encourage others to engage in discussions and research to foster a deeper appreciation of this important part of history.
Support Organizations Working for Justice: Engage with groups that are working to combat racism, promote equality, and provide support to victims of slavery. Your contributions can help create a more just and equitable society.
FAQs
A: The slaves were forced to work on European colonies in the Americas, on sugar plantations in the Caribbean and tobacco and cotton plantations in the US
A: Some of the major African civilizations that were impacted included the Ashanti, the Benin Kingdom, the Kingdom of Kongo, and the Songhai Empire.
A: The trans-Atlantic slave trade spanned over four centuries, officially beginning in the 16th century and ending in the 19th century.
Africa And The Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade
Conclusion
The trans-Atlantic slave trade remains a sobering reminder of the horrors humans are capable of inflicting on each other. By acknowledging and understanding this painful chapter in history, we can work together to build a more just and harmonious world where all people are valued and respected.
As you have just learned about Africa and the Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade, I would like to ask you: Are you interested in learning more about other historical events that have shaped our world?
If so, let me know in the comments below, and I will be happy to explore more topics with you.






