Introduction
South Africa, as an economic powerhouse on the African continent, actively engages in global trade. Its strategic location, abundant natural resources, and strong infrastructure make it an attractive hub for international commerce. Understanding the country’s major trade partners provides invaluable insights into South Africa’s economic landscape and its role in the global marketplace. In this article, we delve into the biggest trade partners of South Africa, highlighting their significance and examining the factors driving these economic partnerships.
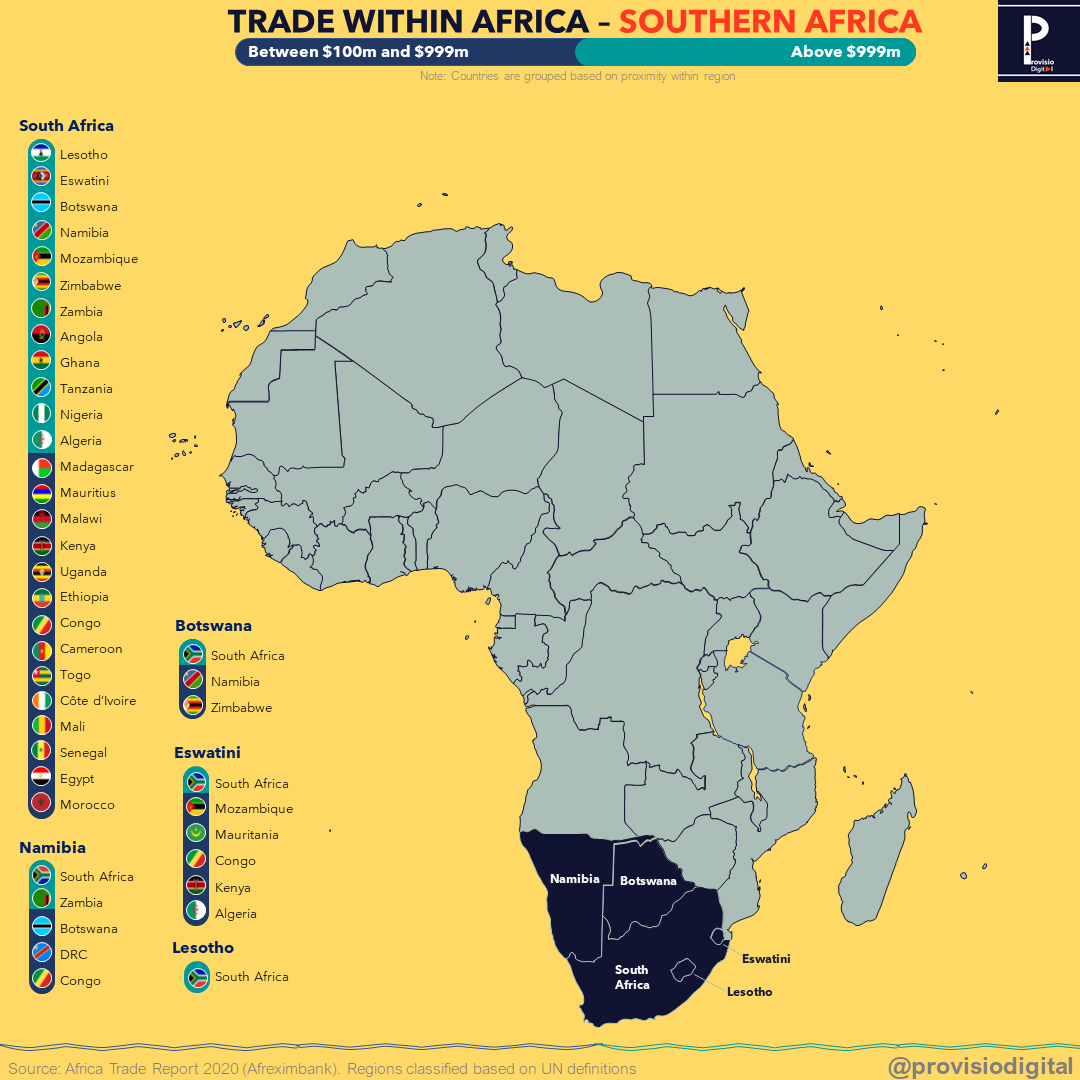
Image: provisioservices.com
China: A Dominant Trade Ally
China stands as South Africa’s largest trade partner, accounting for a substantial portion of the country’s exports and imports. The robust trade relationship between the two nations is fueled by China’s insatiable demand for South African minerals, such as iron ore, coal, and platinum. Moreover, South Africa imports a wide range of manufactured goods from China, including machinery, electronics, and textiles. The strong economic ties between the two countries have spurred significant investment from China in South African infrastructure, energy, and mining sectors.
The European Union: A Historical Partner
The European Union (EU) remains a vital trade partner for South Africa, fostering a mutually beneficial economic relationship. The EU is a major market for South African exports, particularly agricultural products, citrus fruits, and wine. In return, South Africa imports vehicles, machinery, and pharmaceuticals from the EU. Notably, the EU has been a key player in supporting South Africa’s development through investments, aid, and technical assistance.
United States: A Strategic Trade Connection
The United States plays a significant role as one of South Africa’s top trade partners. The two countries share a common interest in fostering economic growth and prosperity. South Africa exports minerals, agricultural products, and manufactured goods to the US, while the US exports machinery, transportation equipment, and chemicals to South Africa. The strategic partnership between the two nations extends beyond trade, encompassing diplomatic and security cooperation.
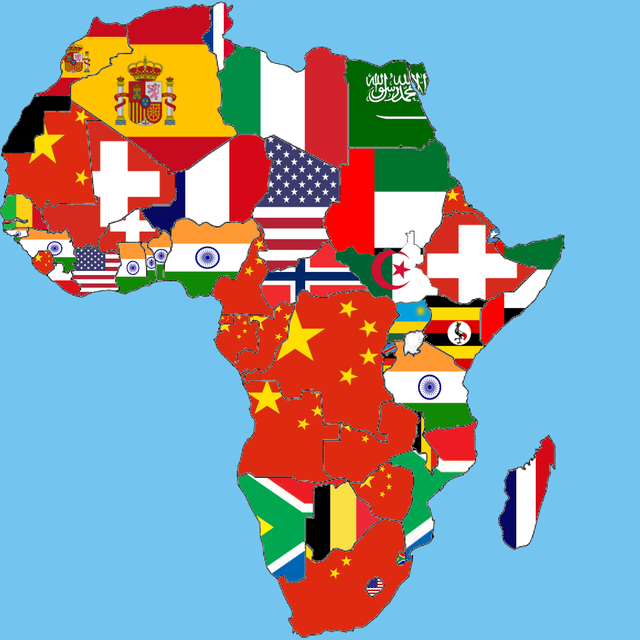
Image: mapsontheweb.zoom-maps.com
Intra-African Trade: A Growing Force
South Africa actively engages in regional trade with countries within the Southern African Development Community (SADC) and the African Union (AU). Intra-African trade plays a crucial role in promoting economic integration, boosting regional development, and reducing reliance on external markets. South Africa exports manufactured goods, agricultural products, and vehicles to neighboring countries, while it imports raw materials, consumer goods, and energy from its African partners. The growth of intra-African trade holds immense potential for South Africa to strengthen its position as a leading economic force on the continent.
India: A Rising Trade Power
India is emerging as a significant trade partner for South Africa, with growing bilateral trade volumes. India imports coal, minerals, and agricultural products from South Africa, while South Africa imports pharmaceuticals, machinery, and textiles from India. The two countries have identified areas for collaboration in sectors such as defense, technology, and infrastructure. India’s growing economic clout and South Africa’s need for investment and innovation make it a promising partnership.
Japan: A Stable and Reliable Partner
Japan maintains a stable and reliable trade relationship with South Africa, with a focus on automotive manufacturing, mining, and infrastructure. Japan imports a substantial quantity of South African coal, iron ore, and platinum, while South Africa imports vehicles, electronics, and machinery from Japan. The two countries share a long history of economic cooperation, and Japanese companies have made significant investments in South Africa’s automotive industry.
Biggest Trade Partners Of South Africa
Conclusion
Understanding South Africa’s biggest trade partners offers a comprehensive view of the country’s economic landscape. These partnerships are driven by a combination of factors, including resource endowments, market access, and strategic alliances. South Africa benefits from these partnerships through export markets for its products, access to imports, and foreign investment. As the global economic landscape evolves, South Africa is well-positioned to leverage its existing trade relationships and strengthen its position as a pivotal player in international commerce. By fostering mutually beneficial economic partnerships, South Africa can continue to drive economic growth, create employment opportunities, and enhance its role in shaping the global economy.






