Introduction
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) plays a pivotal role in safeguarding the stability and integrity of the Indian economy. Among its multifarious responsibilities, forex management stands as a cornerstone, ensuring a stable exchange rate that facilitates international trade and investments.

Image: www.financialexpress.com
In this comprehensive article, we delve into the intricacies of the RBI’s role in forex, exploring its historical evolution, key functions, challenges, and impact on the Indian economy. By shedding light on this crucial aspect of the RBI’s mandate, we aim to enhance our understanding of its significance and appreciate the complexities of India’s monetary system.
Historical Context
The RBI’s involvement in forex management dates back to the pre-independence era. The Currency Act of 1899 established the Indian Currency Board, tasked with maintaining the gold parity of the Indian currency. Post-independence, the RBI was established in 1935, inheriting the responsibilities of the Currency Board.
Key Functions in Forex
The RBI plays a multifaceted role in managing India’s forex reserves, including:
- Regulating the foreign exchange market: The RBI establishes guidelines for the forex market, governing the eligibility of participants, transaction limits, and reporting requirements.
- Managing the exchange rate: The RBI intervenes in the forex market to influence the exchange rate and maintain stability. It buys or sells foreign currencies to prevent excessive volatility or misalignment.
- Building and maintaining forex reserves: The RBI accumulates forex reserves through various means, such as foreign exchange earnings, foreign direct investment, and borrowing. These reserves provide a buffer against external shocks and ensure the country’s ability to meet its international payment obligations.
- Facilitating trade and investment: By managing forex reserves and regulating the market, the RBI facilitates international trade and investment. It ensures a stable exchange rate, reducing currency risk for businesses and investors.
Challenges and Developments
The RBI’s forex management faces several challenges, including:
- Global economic uncertainty: External factors, such as economic crises, geopolitical events, and changes in monetary policies in other countries, can impact India’s exchange rate and forex reserves.
- Demand for foreign currency: The RBI must ensure adequate supply of foreign currency to meet the demand from importers, travelers, and foreign investors.
- Speculation and volatility: The forex market is prone to speculation, which can lead to sudden fluctuations in the exchange rate. The RBI implements measures to mitigate this volatility.
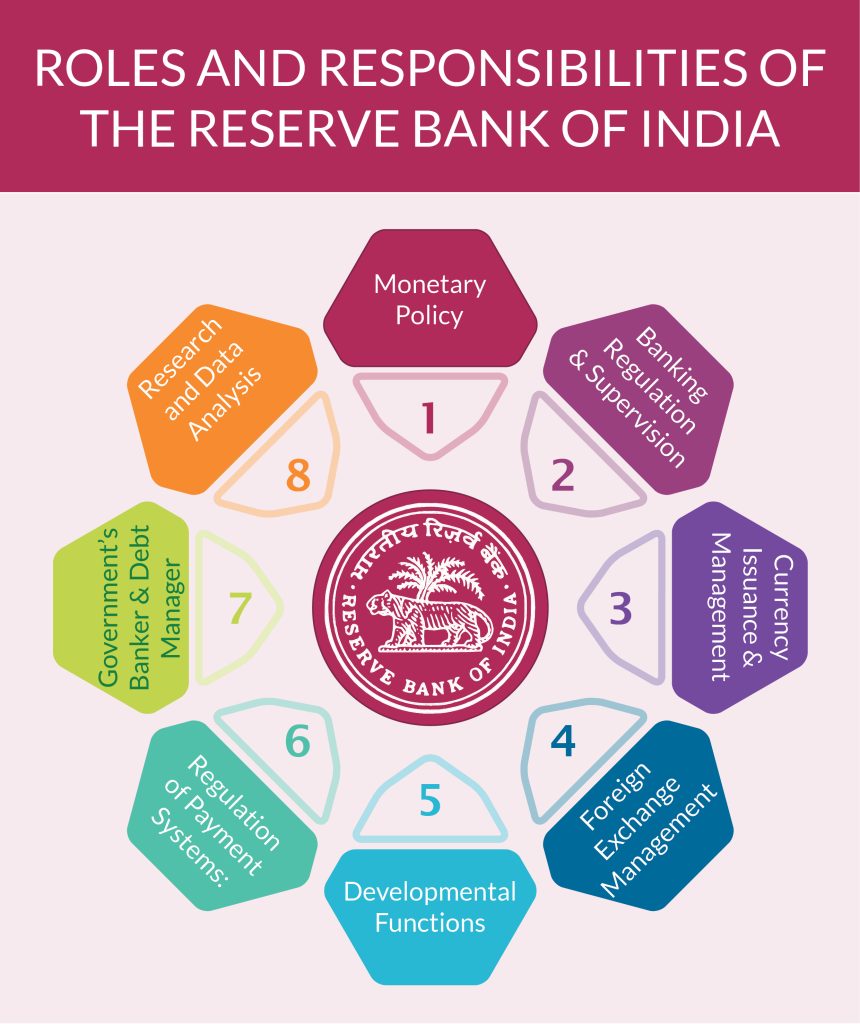
Image: www.ixambee.com
Impact on the Indian Economy
The RBI’s forex management has a significant impact on the Indian economy:
- Stable exchange rate: A stable exchange rate reduces currency risk for businesses and investors, facilitating international trade and capital flows.
- Stable financial system:Forex reserves provide a cushion against external shocks, enhancing the resilience of the financial system.
- Control over inflation: The RBI uses forex reserves to manage the monetary base, contributing to inflation control.
- External debt management: The RBI’s forex reserves help the government meet external debt obligations and improve the country’s creditworthiness.
Role Of Rbi In Forex
Conclusion
The RBI’s role in forex management is essential for maintaining the stability and growth of the Indian economy. By regulating the forex market, managing the exchange rate, building forex reserves, and facilitating international trade and investment, the RBI ensures a conducive environment for economic prosperity.
As the global economy evolves, the RBI continues to adapt its forex management strategies to meet new challenges. Its commitment to maintaining a stable and resilient exchange rate and financial system is crucial for the continued growth and development of the Indian economy.






