Introduction
Inflation, a ubiquitous economic term, holds immense significance in our daily lives. In South Africa, it has been an emotional rollercoaster, impacting citizens’ purchasing power and overall well-being. This article aims to provide a comprehensive exploration of South Africa’s inflation, its causes, consequences, and potential solutions, empowering readers with valuable insights and actionable steps.
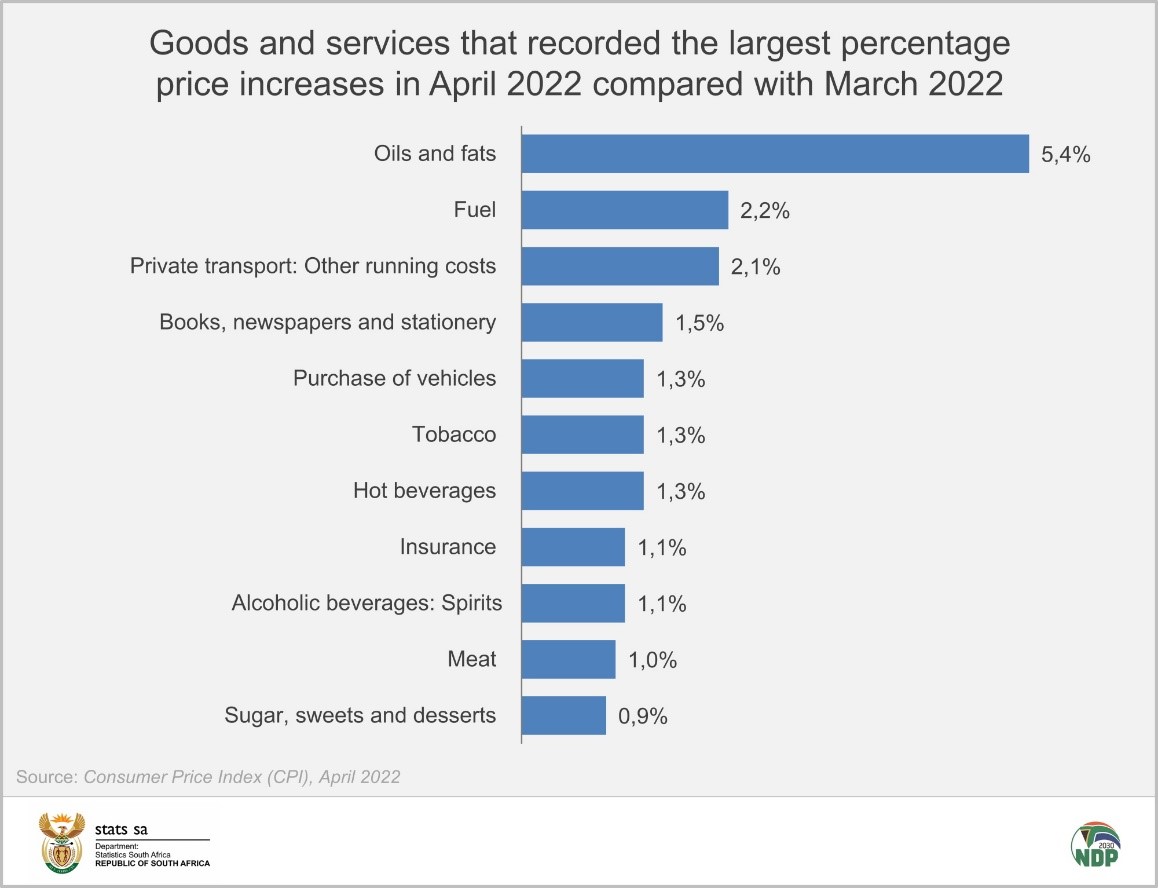
Image: www.statssa.gov.za
Understanding Inflation
Inflation refers to a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services over time. It erodes the purchasing power of money, leading to a decline in the value of savings and investments. Inflation can be caused by various factors, including excess demand, supply shocks, and government policies.
South Africa’s Inflationary Landscape
South Africa has experienced significant inflation over the past few decades, with the rate fluctuating between 2% and 10%. This volatility has posed challenges for consumers, businesses, and policymakers alike. The latest inflation figures indicate a moderate rate of 4.5%, but concerns linger over its upward trajectory.
Causes of Inflation in South Africa
The primary causes of inflation in South Africa include:
-
Excess Demand: Strong economic growth and low unemployment rates have driven up demand for goods and services.
-
Supply Shocks: Disruptions in the global supply chain, natural disasters, and geopolitical tensions have led to higher production costs and reduced supply.
-
Government Policies: Fiscal and monetary policies, such as budget deficits and low interest rates, can also contribute to inflation.

Image: analisagold.com
Consequences of Inflation
Inflation has a profound impact on the South African economy and its citizens:
-
Erosion of Purchasing Power: Rising prices reduce the purchasing power of households, making it more challenging to afford essential goods and services.
-
Lower Investment Returns: Inflation erodes the real returns on savings and investments, discouraging long-term capital accumulation.
-
Business Challenges: Businesses face higher input costs, which can erode profitability and stifle growth.
Expert Insights and Actionable Tips
To address inflation effectively, the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) and government have implemented various measures. Experts emphasize the need for a coordinated approach involving fiscal discipline, targeted monetary policy, and supply-side reforms. Additionally, consumers can make informed financial decisions, such as:
-
Prioritizing Essential Spending: Focusing on necessities and cutting back on non-essential expenses can help mitigate the impact of inflation.
-
Exploring Alternative Investments: Diversifying investments into inflation-resistant assets, such as real estate or gold, can protect against purchasing power loss.
Trading Economics South Africa Inflation
Conclusion
Inflation in South Africa remains a complex and multifaceted issue. By understanding its causes, consequences, and potential solutions, we can navigate its challenges and strive for economic stability. The South African government, businesses, and individuals must work together to implement effective measures that will restore purchasing power, stimulate economic growth, and ultimately create a more prosperous future for all. Let us embrace the lessons learned from South Africa’s inflationary journey and empower ourselves to navigate this economic rollercoaster with resilience and determination. Remember, the power to shape our financial destiny lies within our collective actions.






