Introduction
Have you ever wondered how stock market indices like the S&P 500 or Dow Jones Industrial Average are calculated? These widely followed benchmarks represent the performance of a large basket of stocks, but their calculation goes beyond simply averaging the prices of all the constituent companies. Instead, a value-weighted approach is used, giving greater influence to larger companies with higher market capitalizations. Understanding this calculation is crucial for investors who want to track market performance accurately and make informed investment decisions.

Image: study.com
Defining Value Weighted Index
A value-weighted index is a stock market index that assigns a weight to each constituent company based on its market capitalization. Market capitalization is calculated by multiplying the company’s current stock price by the number of shares outstanding. Companies with larger market capitalizations receive higher weights in the index, meaning they have a greater influence on its overall value.
Calculating a Value Weighted Index
To calculate a value-weighted index, you can follow these steps:
- Identify the constituent companies of the index: Determine the list of companies included in the index.
- Determine the market capitalization of each company: Multiply the current stock price by the number of shares outstanding for each company.
- Calculate the total market capitalization of the index: Sum the market capitalizations of all the constituent companies.
- Calculate each company’s weight in the index: Divide each company’s market capitalization by the total market capitalization of the index.
- Multiply the stock prices by their respective weights: Multiply the current stock price of each company by its weight in the index.
- Sum the weighted stock prices: Add the values obtained in step 5 for all the constituent companies.
- Divide by the sum of weights: Divide the result in step 6 by the sum of all the weights to obtain the value of the index.
Example of Calculating a Value Weighted Index
Suppose we have an index with three constituent companies:
| Company | Stock Price | Number of Shares Outstanding | Market Capitalization | Weight in Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apple | $150 | 1 billion | $150 billion | 0.5 |
| Microsoft | $100 | 1.2 billion | $120 billion | 0.4 |
| Amazon | $120 | 0.8 billion | $96 billion | 0.3 |
- Total Market Capitalization = $150 billion + $120 billion + $96 billion = $366 billion
- Apple’s Weight = $150 billion / $366 billion = 0.41
- Microsoft’s Weight = $120 billion / $366 billion = 0.33
- Amazon’s Weight = $96 billion / $366 billion = 0.26
- Value of Index = (0.41 x $150) + (0.33 x $100) + (0.26 x $120) = $133.4
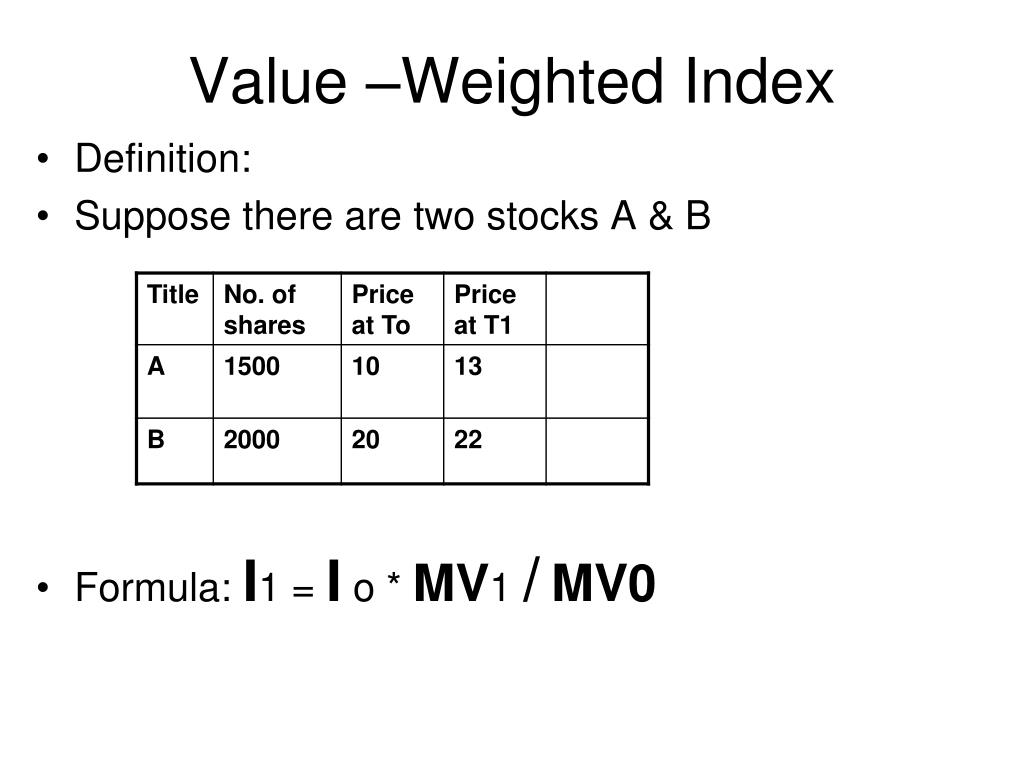
Image: www.slideserve.com
Importance of Value Weighting
Value weighting ensures that larger companies have a greater influence on the index. This is because larger companies tend to be more stable and have more diversified revenue streams, which reduces the overall volatility of the index. For investors looking for a broad representation of the stock market, a value-weighted index provides a reliable measure of market performance.
Applications of Value Weighted Indices
- Performance Benchmarking: Value-weighted indices serve as a benchmark against which fund managers and other investors can compare the performance of their portfolios.
- Asset Allocation: Investors may allocate their assets based on the performance of value-weighted indices. For example, an investor may allocate more funds to a sector if its corresponding value-weighted index is performing well.
- Portfolio Diversification: By tracking a value-weighted index, investors can diversify their portfolios across various sectors and market capitalizations.
How To Calculate Value Weighted Index
Conclusion
Understanding how a value-weighted index is calculated is essential for investors seeking a comprehensive view of market performance. By assigning higher weights to larger companies, value-weighted indices provide a weighted representation of the stock market. Utilizing this calculation method enables investors to make informed decisions when constructing and managing their portfolios.






